Rubber Tyred Gantry Crane Foam Filled Tire Bead Cracking Repair: Proven Methods
Table of Contents
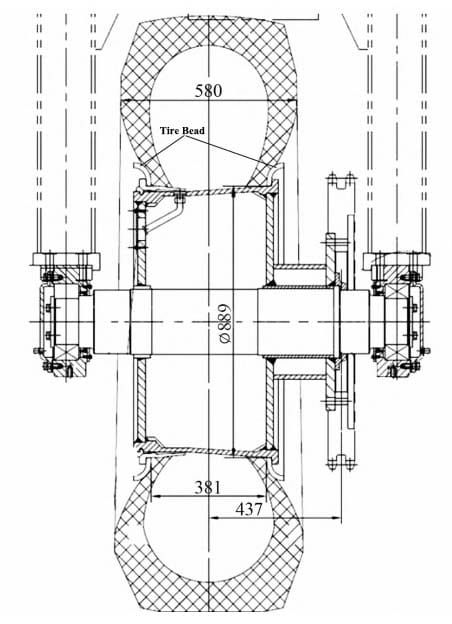
As container terminals’ main loading and unloading equipment, rubber tyred gantry crane have good mobility. Usually, a single-tire rubber tyred gantry crane is equipped with 8 tires. However, tire rubber tyred gantry crane face daily problems such as leaking tires, bulging, and damage. Daily management personnel invest a lot, and cannot prevent or avoid the safety risks caused by flat tires, which greatly impact normal operations. The tire-filling process can effectively solve the problems of pneumatic tires, but after the tire-filling process is completed, the foam-filled tire bead may crack. The cracked foam-filled tire bead must be repaired in time to prevent the foam filled tire bead from breaking.
Analysis of the Cause Rubber Tyred Gantry Crane Foam Filled Tire Bead Cracking
The foam-filled tire bead is assembled between the two sides of the tire and the rim, which mainly plays the role of fixing the tire.
With the increase in the service life of foam-filled tire beads, some tires have cracked With the increase in the service life of foam filled tire beads, some tires have cracked retaining rings one after another. When the crack in the foam-filled tire bead develops to a certain extent, the retaining ring will be completely disconnected and cannot play the role of fixing the tire.
At this time, the tire of rubber tyred gantry crane is not suitable for continued use. Due to the rubber filling of the tire, the retaining ring cannot be replaced for the tire whose retaining ring is disconnected. At this time, the retaining ring is severely deformed and cannot be restored to its original position. Maintenance cannot be carried out, resulting in the entire rubber-filled tire being scrapped (including the tire itself and the colloid filled inside the tire), resulting in greater losses. Compared with pneumatic tires, the cracking of the retaining ring is concentrated on rubber-filled tires.
Compared with pneumatic tires, rubber-filled tires have poor elasticity and poor cushioning of the vibration load of the equipment. Therefore, when the equipment is running, the tire retaining ring is subjected to a relatively large force, causing the retaining ring to crack. one after another. When the crack in the foam-filledtire bead develops to a certain extent, the retaining ring will be completely disconnected and cannot play the role of fixing the tire.
At this time, the tire is not suitable for continued use. Due to the rubber filling of the tire, the retaining ring cannot be replaced for the tire whose retaining ring is disconnected. At this time, the retaining ring is severely deformed and cannot be restored to its original position.
Maintenance cannot be carried out, resulting in the entire rubber-filled tire being scrapped (including the tire itself and the colloid filled inside the tire), resulting in greater losses. Compared with pneumatic tires, the cracking of the retaining ring is concentrated on rubber-filled tires. Compared with pneumatic tires, rubber-filled tires have poor elasticity and poor cushioning of the vibration load of the equipment. Therefore, when the equipment is running, the tire retaining ring is subjected to a relatively large force, causing the retaining ring to crack.
Rubber Tyred Gantry Crane Foam Filled Tire Bead Cracking Repair requirements
From the cause of the cracking of the foam-filled tire bead, it can be seen that the strength of the retaining ring needs to be improved, and the maintenance plan needs to meet the following 5 requirements:
- Due to the rubber filling of the tire, the retaining ring cannot be disassembled, and maintenance needs to be carried out on the rubber-filled tire assembly.
- Prevent the cracks from spreading further.
- Repair and deal with cracks.
- Improve the overall strength of the foam-filled tire bead.
- Try to avoid or reduce damage to the tires during maintenance.
Rubber Tyred Gantry Crane Foam Filled Tire Bead Cracking Maintenance measures
(1) Crack drilling, anti-expansion. Drill holes at the ends of the cracks to prevent further expansion of the cracks. When drilling, pay attention to controlling the strength and depth of the drill to avoid the drill bit from damaging the tire.
(2) Crack grinding and maintenance. The grinding head of an electric grinder is used to grind the cracks and weld them. The depth of crack grinding is controlled in a suitable position to prevent the tire wall in this part from being directly exposed to more heat during welding operations, which can cause tire damage.
(3) Design and produce auxiliary reinforced retaining rings. Used for 61 t tire crane 21. 00-35 Tire retaining ring, for example, design auxiliary retaining ring. When designing the auxiliary retaining ring, the designed retaining ring and the original retaining ring need to be considered.
The fit is good, and the upper and lower edges need to have enough welding space after installation. The designed retaining ring itself needs to have a certain strength. The thickness of the retaining ring is selected to be 14 mm, and 10 mm welding space is reserved for the upper and lower parts.
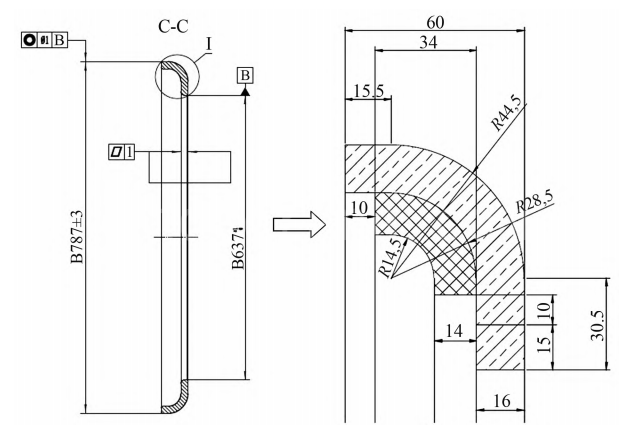
The designed retaining ring is only welded to the original retaining ring to strengthen the strength of the original retaining ring and is not related to other locations of the wheel hub. When the tire is damaged for other reasons, the tire can be disassembled by the normal process, and the other parts of the wheel hub can still be used normally. The original retaining ring is made of manganese steel. Considering the strength of the retaining ring and the needs of the welding process, the reinforced retaining ring is made of Q345B steel plate.
(4) Welding assistance to strengthen the retaining ring. Install the designed auxiliary retaining ring inside the original retaining ring and fix it by welding. For the retaining ring without the sprocket side, the auxiliary reinforced retaining ring can be installed directly on the retaining ring as a whole and welded; for the retaining ring with the sprocket side, the auxiliary reinforced retaining ring cannot be installed directly.
The customized retaining ring needs to be cut in half. The installation of the retaining ring can be completed without disassembling the sprocket, and then welding and fixing are implemented, and the cut parts are welded together. To ensure the welding quality and improve the operability, the following 3. The 2mm 507 electrode is welded with a DC welding machine; to reduce the damage caused by welding to the tire, segmented welding is used to disperse the heat, and the welding site is watered appropriately along the outside of the retaining ring to speed up the heat dissipation and cool the tires at the welding site.
(5) Paint to prevent corrosion. Clean up the welding parts and paint them to prevent the welds from rusting and extend the service life.
Conclusion
Under the above maintenance technology, the repair of the rubber-filled tire retaining ring cracking was completed. During the period, there was no damage to the rubber-filled tire caused by the re-cracking or disconnection of the retaining ring, which eliminated the safety risks caused by the cracking of the tire retaining ring and effectively guaranteed the safety of the tire. For the problem of cracking the retaining ring of the rubber-filled tire, a thickened retaining ring can be selected when assembling the tire after filling the rubber to reduce the probability of cracking the foam-filled tire bead.
Send Your Inquiry
- Email: sales@hndfcrane.com
- WhatsApp: +86 191 3738 6654
- Telegram: +86 191 3738 6654
- Tel: +86-373-581 8299
- Fax: +86-373-215 7000
- Add: Changnao Industrial District, Xinxiang City, Henan Province, China
 WeChat
WeChat




























































































































